Table of Contents
Introduction
The healthcare industry is undergoing a rapid transformation, fueled by technological advancements that promise to enhance patient care, streamline processes, and reduce costs. As we move further into the digital age, several technology trends are emerging as game-changers in the healthcare sector. In this blog, we will explore the top five technology trends that are shaping modern healthcare and discuss their impact on the industry.

1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
What Is AI in Healthcare?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming healthcare by providing tools that enable predictive analytics, personalized treatment plans, and improved patient outcomes. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from various sources, such as electronic health records (EHRs), medical imaging, and genetic information, to identify patterns and make accurate predictions. These capabilities help healthcare professionals make informed decisions quickly and accurately.
Key Applications:
Predictive Analytics: AI models can predict patient readmissions, disease outbreaks, and other healthcare events, enabling preventive measures and reducing healthcare costs.
Diagnostic Accuracy: AI-powered systems can detect diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and heart conditions with high accuracy by analyzing medical images and patient data. For example, Google’s AI algorithm has shown remarkable success in diagnosing diabetic retinopathy from eye scans.
Personalized Medicine: AI can analyze genetic and clinical data to develop personalized treatment plans, ensuring that patients receive therapies that are most effective for their specific conditions.
Case Study:
A notable example of AI’s impact is IBM Watson’s collaboration with Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. Watson uses AI to analyze vast amounts of medical data to provide oncologists with evidence-based treatment recommendations for cancer patients. This has resulted in more accurate and efficient cancer treatment plans, leading to better patient outcomes.
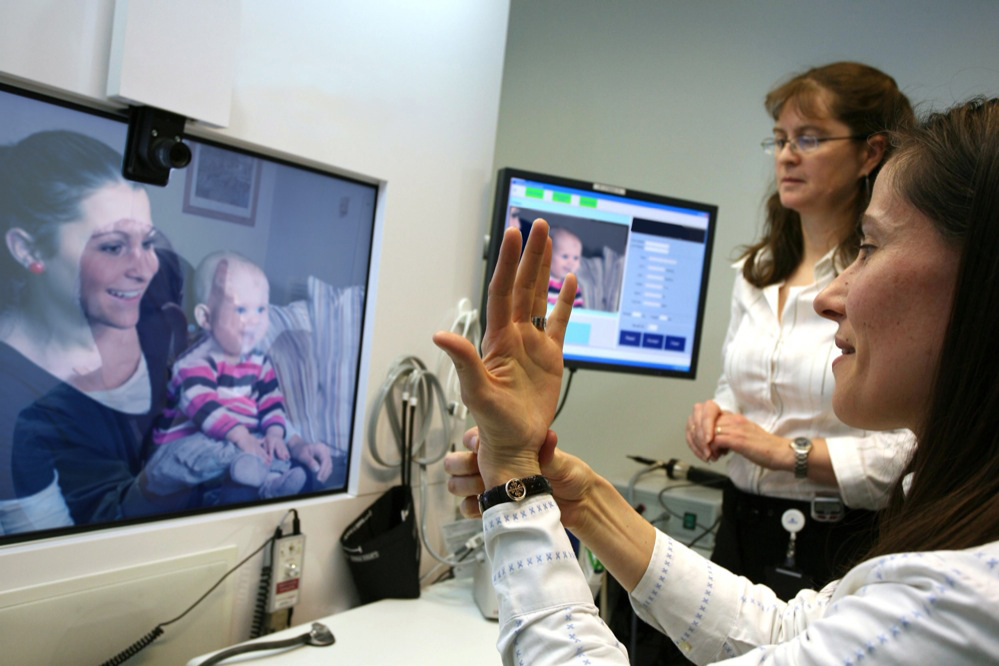
2. Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring
What Is Telemedicine?
Telemedicine refers to the delivery of healthcare services remotely using telecommunications technology. It allows patients to consult with healthcare providers through video calls, phone calls, and online messaging, eliminating the need for physical visits. Remote patient monitoring involves the use of wearable devices and sensors to collect and transmit health data to healthcare professionals in real time.
Key Applications:
- Virtual Consultations: Patients can connect with doctors remotely for routine check-ups, follow-ups, and consultations, making healthcare more accessible, especially in rural and underserved areas.
- Chronic Disease Management: Remote monitoring devices, such as blood pressure monitors and glucose sensors, allow healthcare providers to track patients’ conditions continuously, providing timely interventions when necessary.
- Post-Surgical Care: Telemedicine enables post-operative patients to recover at home while remaining under the supervision of healthcare professionals through virtual check-ins and monitoring devices.
Case Study:
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telemedicine. For instance, the Cleveland Clinic reported a 78-fold increase in virtual visits between March 2020 and April 2020. This surge highlighted the effectiveness of telemedicine in providing essential healthcare services during emergencies, ensuring patient safety, and reducing the burden on healthcare facilities.
3. Wearable Health Devices
What Are Wearable Health Devices?
Wearable health devices are electronic gadgets worn on the body to monitor health metrics such as heart rate, activity levels, sleep patterns, and more. These devices include smartwatches, fitness trackers, and specialized medical wearables designed to monitor specific health conditions.
Key Applications:
- Fitness and Wellness Tracking: Wearables like Fitbit and Apple Watch monitor physical activity, sleep quality, and overall fitness levels, encouraging users to lead healthier lifestyles.
- Continuous Health Monitoring: Medical-grade wearables, such as ECG monitors and glucose monitors, provide continuous monitoring of vital signs, enabling early detection of health issues.
- Elderly Care: Wearables equipped with fall detection and emergency alert features provide safety and peace of mind for elderly individuals, ensuring timely assistance in case of emergencies.
Case Study:
The Oura Ring, a wearable health device, gained popularity for its ability to monitor sleep patterns, heart rate variability, and body temperature. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the NBA used Oura Rings to monitor players’ health and detect early signs of illness, helping prevent outbreaks and ensuring the safety of athletes.

4. Blockchain in Healthcare
What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized and secure digital ledger technology that records transactions across multiple computers. In healthcare, blockchain can enhance data security, interoperability, and transparency, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of patient information.
Key Applications:
- Secure Medical Records: Blockchain allows for the secure storage and sharing of electronic health records (EHRs), ensuring that patient data is tamper-proof and accessible only to authorized parties.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can track the movement of pharmaceuticals from manufacturers to patients, reducing the risk of counterfeit drugs and ensuring the authenticity of medications.
- Clinical Trials and Research: Blockchain facilitates the secure sharing of clinical trial data and research findings, promoting collaboration and transparency in medical research.
Case Study:
MediLedger, a blockchain-based platform, is used in the pharmaceutical industry to track the supply chain of drugs. It ensures that counterfeit medications are identified and removed from the supply chain, safeguarding patient safety and maintaining trust in the healthcare system.

5. 3D Printing in Healthcare
What Is 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, involves creating three-dimensional objects from digital models by layering materials. In healthcare, 3D printing is used to produce custom prosthetics, implants, and even human tissues, revolutionizing personalized medicine and surgical procedures.
Key Applications:
- Custom Prosthetics and Implants: 3D printing allows for the creation of customized prosthetics and implants that fit patients perfectly, enhancing comfort and functionality.
- Surgical Planning and Training: Surgeons can use 3D-printed models of patients’ anatomy to plan complex surgeries with precision, reducing risks and improving outcomes.
- Bioprinting: 3D printing of living tissues and organs holds the promise of creating transplantable organs, potentially eliminating organ shortages in the future.
Case Study:
A significant example of 3D printing in healthcare is the creation of a 3D-printed titanium rib cage for a cancer patient in Spain. The customized implant provided an exact fit, improving the patient’s recovery and quality of life. This case demonstrated the potential of 3D printing to revolutionize complex surgical procedures.
Conclusion
The healthcare industry is undergoing a transformation driven by technological advancements. AI and machine learning, telemedicine, wearable health devices, blockchain, and 3D printing are reshaping the way healthcare is delivered, making it more efficient, personalized, and accessible. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will play a crucial role in improving patient outcomes, reducing healthcare costs, and enhancing the overall quality of care. Embracing these trends will be essential for healthcare providers to stay competitive and meet the changing needs of patients in the modern era.